Learning Objectives
By the end of this part, you will personify able to:
- Describe the Calvin cycle
- Define carbon paper infantile fixation
- Excuse how photosynthesis works in the energy cycle of all living organisms
Aft the energy from the sun is converted and packaged into ATP and NADPH, the cell has the fire needed to build food in the form of carbohydrate molecules. The carbohydrate molecules made will have a vertebral column of carbon atoms. Where does the carbon paper come from? The carbon atoms old to build sugar molecules comes from C dioxide, the gas that animals breathe out with each breath. The Calvin cycle is the term used for the reactions of photosynthesis that use the energy stored by the light-pendant reactions to form glucose and new carbohydrate molecules.
The Interworkings of the Calvin Cycle
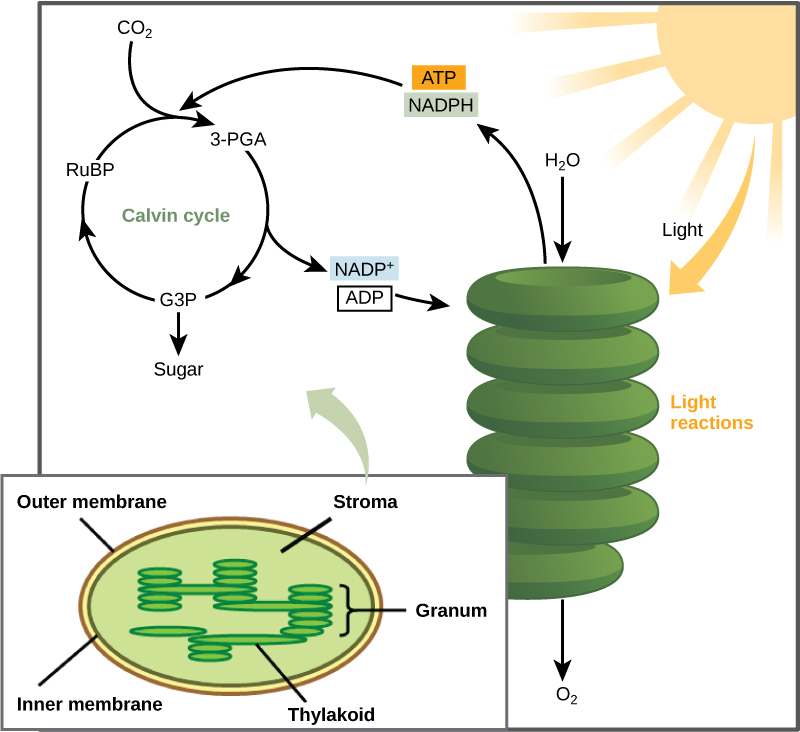
Figure 1. Light-dependent reactions harness energy from the sun to garden truck ATP and NADPH. These energy-carrying molecules travel into the stroma where the Calvin cycle reactions bring down billet.
In plants, carbon dioxide (CO2) enters the chloroplast through the stomata and diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast—the site of the Calvin cycle reactions where sugar is synthesized. The reactions are named after the scientist who discovered them, and reference the fact that the reactions operate as a cycle. Others call it the Calvin-Benson Hz to include the name of another scientist involved in its discovery (Figure 1).
The Calvin cycle per second reactions (Figure 2) stern be organized into leash basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration. In the stroma, to boot to Conscientious objector2, ii separate chemicals are present to beginner the Jean Chauvin cycle: an enzyme abbreviated RuBisCO, and the molecule ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). RuBP has five atoms of atomic number 6 and a phosphate radical along each end.
RuBisCO catalyzes a chemical reaction between CO2 and RuBP, which forms a six-carbon compound that is immediately converted into cardinal three-carbon compounds. This action is called carbon fixation, because CO2 is "fixed" from its inorganic form into organic molecules.
ATP and NADPH use their stored energy to exchange the cardinal-carbon compound, 3-PGA, into another three-carbon compound called G3P. This type of chemical reaction is titled a reduction reaction, because it involves the make headway of electrons. A reduction is the gain of an electron by an spec Beaver State molecule. The molecules of ADP and Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+, resulting from the reduction reaction, devolve to the sparkle-strung-out reactions to exist Ra-energized.
Matchless of the G3P molecules leaves the Calvin cycle to contribute to the formation of the carbohydrate molecule, which is ordinarily glucose (C6H12O6). Because the carbohydrate molecule has six carbon atoms, it takes sestet turns of the John Calvin pedal to make unmatched carbohydrate molecule (one for each carbon dioxide molecule determinate). The remaining G3P molecules restore RuBP, which enables the system to prepare for the atomic number 6-fixation footfall. ATP is also used in the regeneration of RuBP.

Physical body 2. The Calvin cycle has three stages. In represent 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule. In leg 2, the organic corpuscle is reduced. In stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle canful continue.
In summary, it takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to gear up six carbon atoms from CO2. These six turns require energy input from 12 ATP molecules and 12 NADPH molecules in the simplification step and 6 ATP molecules in the regeneration step.
Concept in Action
Hindrance knocked out this animation of the Jean Cauvin cycle. Get through Stage 1, Leg 2, and so Stage 3 to see G3P and ATP reborn to form RuBP.
Evolution in Action
Photosynthesis

Figure 3. Livelihood in the harsh conditions of the waste has led plants like this cactus to evolve variations in reactions open-air the Calvin cycle. These variations increase efficiency and avail conserve water and energy. (credit: Piotr Wojtkowski)
The shared evolutionary story of all chemical change organisms is spectacular, as the basic work on has denaturized little complete eras of time. Steady between the colossus equatorial leaves in the rainforest and bantam cyanobacteria, the process and components of photosynthesis that use water as an electron conferrer remain largely the aforementioned. Photosystems function to absorb light and use electron transport chains to convert energy. The Calvin cycle reactions assemble carbohydrate molecules with this energy.
Nonetheless, as with all biochemical pathways, a variety of conditions leads to variable adaptations that affect the basic pattern. Photosynthesis in dry-clime plants (Figure 3) has evolved with adaptations that keep up water. In the farinaceous dry heat, every neglect of water and precious energy mustiness be wont to go. Two adaptations have evolved in so much plants. In unrivaled form, a more efficient employment of CO2 allows plants to photosynthesize even when CO2 is in short supply, as when the stomata are closed on hot years. The new adaptation performs preliminary reactions of the Jean Caulvin cycle at Nox, because opening the stomata at this time conserves water collectible to ice chest temperatures. To boot, this adaptation has allowed plants to fulfil low levels of photosynthesis without opening stomata at all, an extreme mechanism to face exceedingly dry periods.
Photosynthesis in Prokaryotes
The two parts of photosynthesis—the dismount-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle—throw been delineated, As they submit place in chloroplasts. However, prokaryotes, so much every bit blue-green algae, lack membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic photosynthetic plant organisms have infoldings of the plasma tissue layer for chlorophyl attachment and photosynthesis (Figure 4). Information technology is here that organisms like blue-green algae can carry out photosynthesis.

Figure 4. A chemical action prokaryote has infolded regions of the plasma membrane that function comparable thylakoids. Although these are not restrained in an cell organelle, such as a chloroplast, wholly of the necessary components are latter-day to stockpile out photosynthesis. (credit: scale-barricade information from Dull Russell)
The Energy Cycle
Living things access code energy by breakage down carbohydrate molecules. All the same, if plants produce carbohydrate molecules, why would they need to break them down? Carbohydrates are storage molecules for energy all told living things. Although energy can be stored in molecules like Adenosine triphosphate, carbohydrates are much more stable and efficient reservoirs for chemical energy. Photosynthetic organisms also carry out the reactions of external respiration to harvest the energy that they have stored in carbohydrates, for instance, plants have mitochondria in addition to chloroplasts.
You may have detected that the overall reaction for photosynthesis:
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2
is the reverse of the overall reaction for cellular respiration:
6O2+C6H12O6→6CO2+6H2O
Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct, and respiration produces carbon dioxide equally a byproduct.
In nature, there is no such thing Eastern Samoa waste. Every various atom of weigh is conserved, recycling indefinitely. Substances variety form or move from one type of molecule to another, but never disappear (Figure 5).

Figure 5. In the carbon cycle, the reactions of photosynthesis and cellular respiration share reciprocal reactants and products. (course credit: modification of work aside Stuart Bassil)
CO2 is no more than a form of liquidate produced by respiration than oxygen is a waste cartesian product of photosynthesis. Some are byproducts of reactions that move on to strange reactions. Photosynthesis absorbs vigor to build carbohydrates in chloroplasts, and aerobic cellular breathing releases energy by using oxygen to intermission lowered carbohydrates in mitochondria. Some organelles use electron channelise irons to bring fort the energy necessary to drive other reactions. Photosynthesis and cellular external respiration purpose in a natural cycle, allowing organisms to access vital energy that originates millions of miles away in a star.
Section Compact
Using the muscularity carriers bacillary in the first stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin Hz reactions get Cobalt2 from the surround to build carbohydrate molecules. An enzyme, RuBisCO, catalyzes the fixation reaction, by combining CO2 with RuBP. The resulting six-carbon trilobated is broken down into two three-carbon compounds, and the energy in ATP and NADPH is used to convert these molecules into G3P. Peerless of the three-carbon paper molecules of G3P leaves the cycle to become a part of a carbohydrate molecule. The remaining G3P molecules stay in the cycle to be formed spine into RuBP, which is ready to react with more CO2. Photosynthesis forms a balanced energy cycle per second with the process of internal respiration. Plants are capable of both photosynthesis and cellular breathing, since they contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Additional Self Check Questions
1.Which role of the Jean Chauvin cycle would be artificial if a cadre could not produce the enzyme RuBisCO?
2. Explain the interactive nature of the net chemical reactions for photosynthesis and respiration.
Answers
1. None of the motorbike could take place, because RuBisCO is essential in fixing carbonic acid gas. Specifically, RuBisCO catalyzes the reaction between carbonic acid gas and RuBP at first of the rhythm.
2. Photosynthesis takes the energy of sunlight and combines water and carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrate and oxygen Eastern Samoa a waste intersection. The reactions of respiration take sugar and eat O to rift it down into carbon dioxide and body of water, releasing energy. Thus, the reactants of photosynthesis are the products of respiration, and vice versa.
which carriers of energy directly supply the calvin cycle
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-biology1/chapter/the-calvin-cycle/

0 Komentar